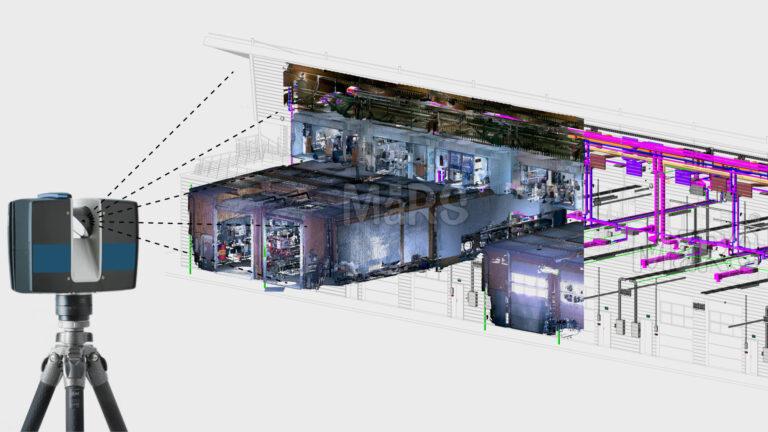
Building information modeling (BIM) is a system that combines project information with 3D object data to minimize errors and inaccuracies. The goal of BIM, which is still in its early stages of development, is to address issues and promote collaboration in the construction industry. The complexity of mechanical, electrical, and plumbing (MEP) systems has raised the need for space and coordination. The coordination of MEP systems is a significant difficulty in buildings due to space constraints, especially in complex structures like high-rise commercial buildings and expansive infrastructures.
The multidisciplinary MEP coordination process that is now in place takes a lot of time and money. To improve coordination and decrease collisions, the emergence of BIM integration with MEP for simplified constructability analysis has been discussed in this article.
BIM Integrated Framework for MEP Constructability
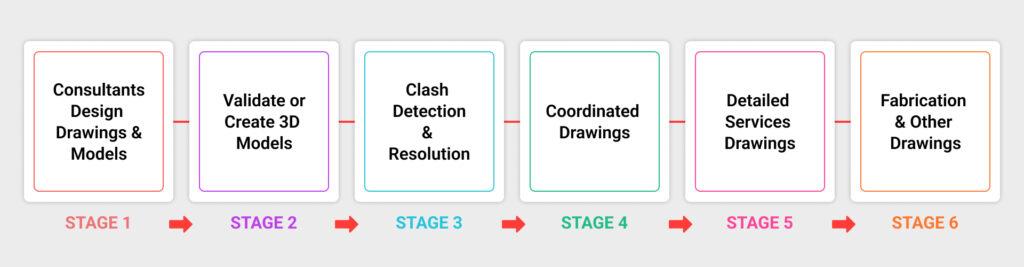
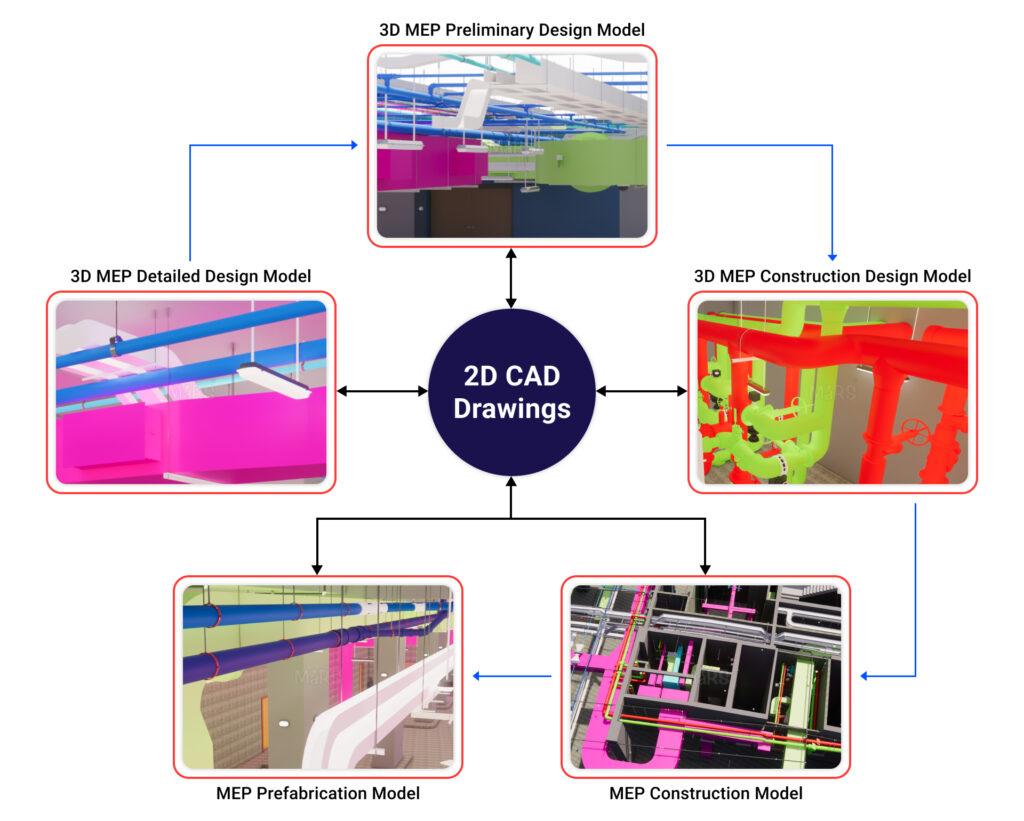
BIM for MEP coordination needs to be integrated from the basic design stage to the building stage, according to prior studies and the opinions of BIM specialists. A useful BIM-enabled MEP layout framework has been created based on the research findings. The framework is made up of five different level-of-detail (LOD) models and the coordinated sequential steps of the MEP layout design process.
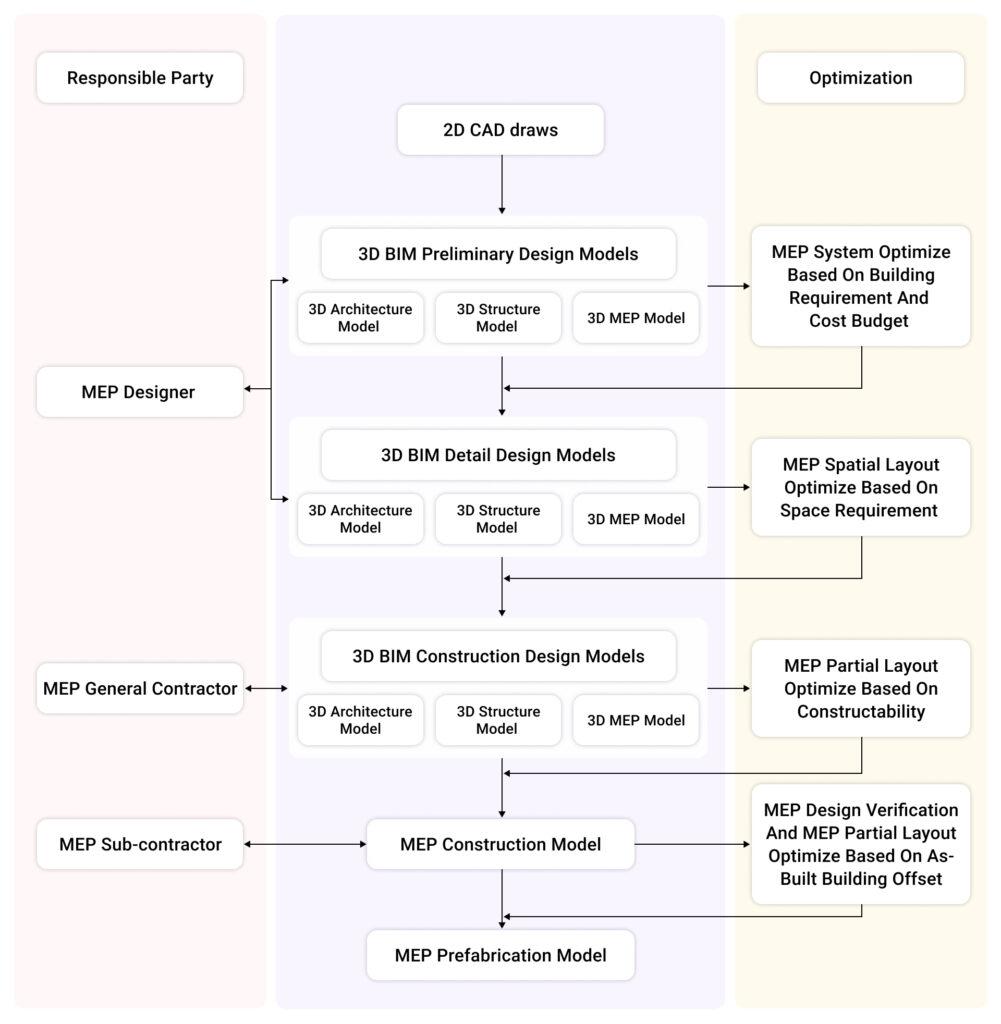
The models and the steps of coordination describing the relationship of the models to one another during the MEP design development are listed below:
1. Preliminary Design Model and System Optimization
Model: Using early project configuration, such as schematics, diagrams, and layouts, the 3D MEP preliminary design model enables MEP designers to automatically compute system load and layout.
System Optimization: During the preliminary design stage of MEP, multiple alternative schemes may be proposed through various methods like sunlight analysis, indoor air quality simulation, energy analysis, and ventilation simulation, with the best scheme chosen to meet cost budget and green building certification standards.
2. Detail Design Model and Spatial Layout Optimization
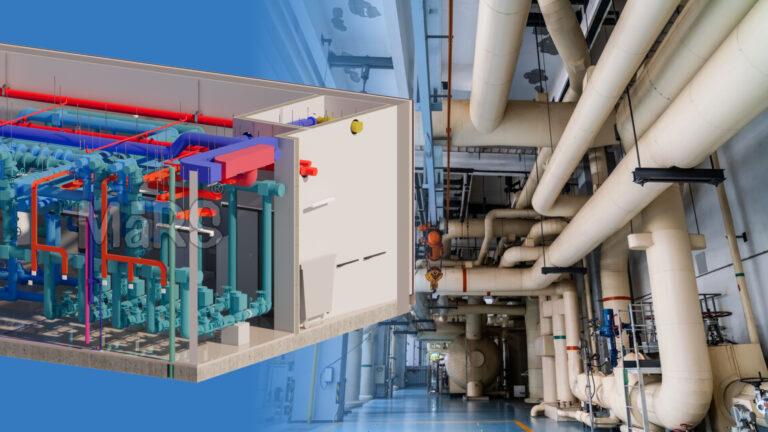
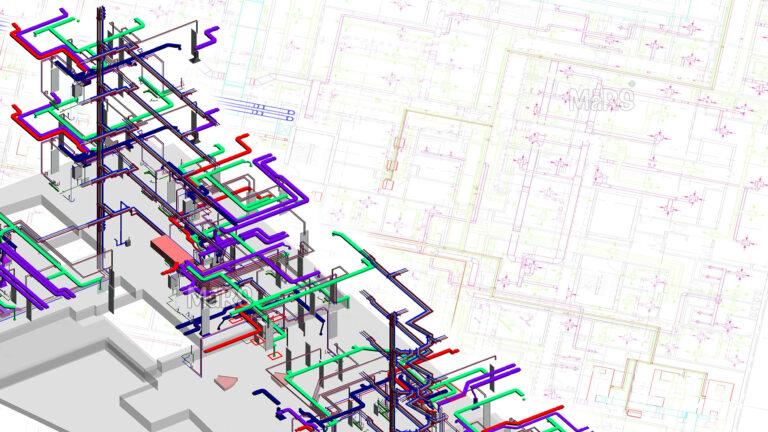
Model: All MEP system design components aside from minor components like wires and sprinklers are detailed in the 3D MEP detail design model. MEP designers can adjust design schemes and coordination by including architectural and structural models.
Spatial Optimization: BIM tools help identify clashes in MEP systems when integrating architecture and structure models. They provide visualization capabilities for specialty trades, designers, and coordinators to review and detect conflicts faster. These tools enable instant changes and trace effects on other components and systems.
3. Construction Design Model and Partial Layout Optimization
Model: The preconstruction stage involves the usage of the MEP construction design model. The model is appropriate for the installation and simulation of the building. In this model, construction tools like scaffolding, supports, and formwork are produced.
Partial Layout Optimization based on Constructability: Taking into account access, configuration, construction strategy, and safety, MEP contractors must assess the constructability of existing design schemes. Based on their expertise in construction, they may designate areas for workers, allow for off-site prefabrication, and improve material handling procedures.
4. MEP Construction Model and Design Verification
Model: This model makes use of design plans, specifications, and knowledge to detect structural and MEP component variances that affect layout design and unify design through building stages, ensuring constructability.
Design Verification and MEP layout coordination: Measuring construction deviations, updating BIM models, analyzing deviations, and modifying the initial design to satisfy construction needs are all part of the most important stages in the MEP design process.
5. MEP Prefabrication Model
This model is appropriate for factory fabrication and assembly since it is based on the MEP construction model and manufacturer-specific information. It contains all production data, allowing for more precise building systems, improved estimations, and direct MEP fabrication.
BIM Application in Constructability Analysis
Constructability is the capacity of design efforts to support efficient construction operations, according to the Construction Industries Research and Information Association (CIRIA). To reduce reworks and ensure effective construction, designers should concentrate on integrating systems like structural and HVAC and addressing interface issues that affect constructability. The following analysis can be made using BIM:
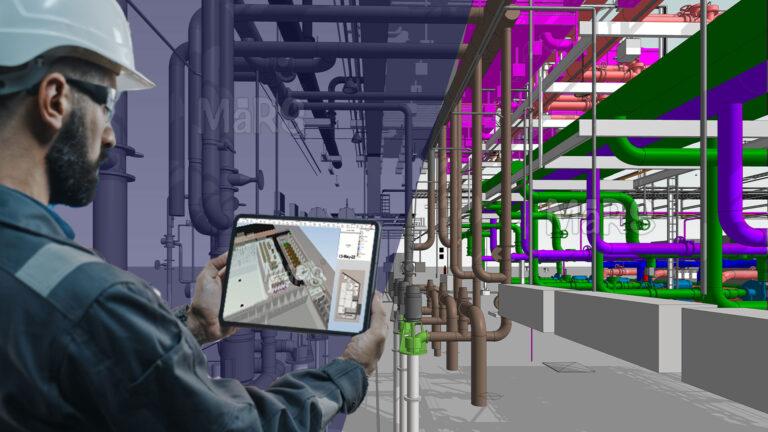
- Spatial Review: Similar to virtual reality, BIM offers a high-performance solution for assessing integrated design content, increasing productivity, and spotting poor spatial allocation designs, making it an indispensable tool for users.
- Measurement Review: By using its database, BIM preserves consistency and streamlines measurement design verification. Designers can use the synchronization feature to rapidly check changes, update drawings, and update annotations in plan view. Measurement check installation is also made simpler by BIM.
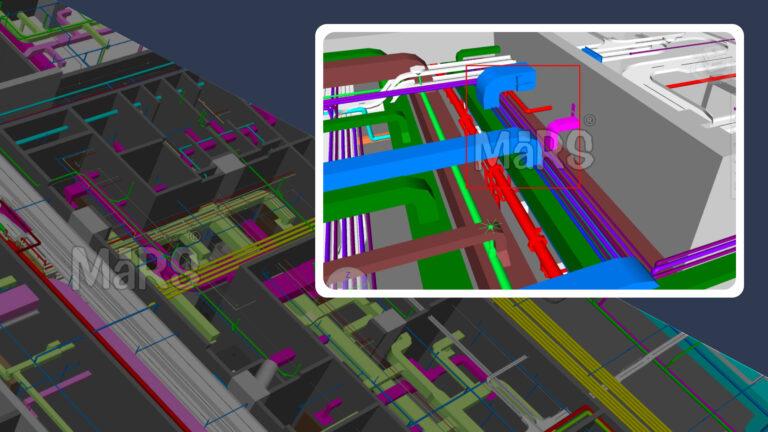
- Clash Detection: Engineers can quickly find and assess conflicts as models are being developed thanks to BIM solutions. With the use of its clash detection feature, potential conflicts are found and a report is produced for evaluation and resolution. By facilitating clash identification and ensuring uniformity, BIM technology improves construction quality.
Conclusion
BIM is an essential tool for determining a design’s constructability before construction, avoiding errors and reworks. It has benefits including simple design problem detection, enhanced communication in a 3D environment, and automatic clash detection, which improves communication performance.