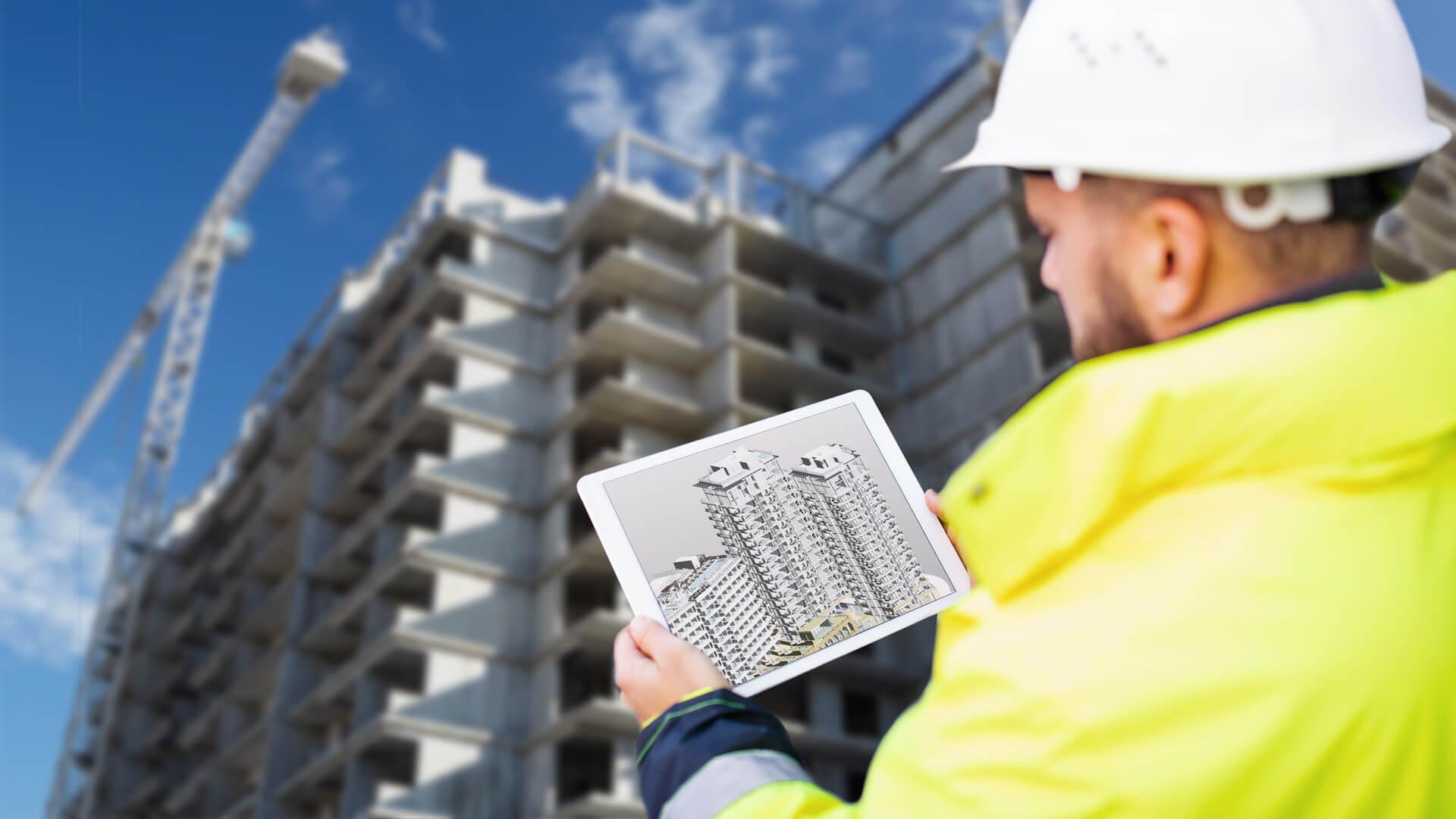
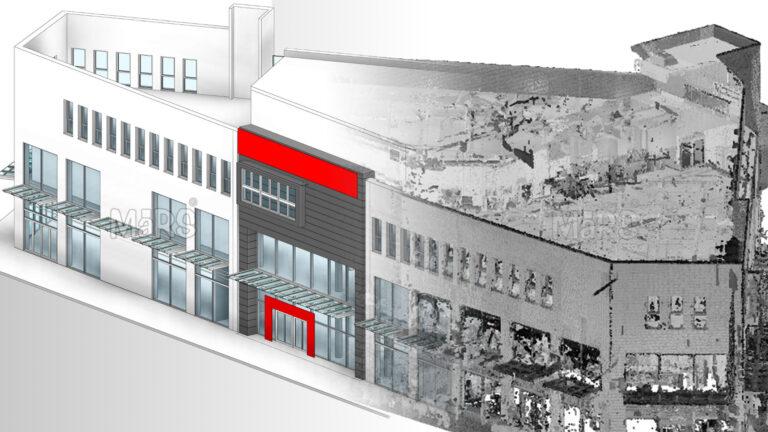
Structural engineers are always looking for new ways to advance and keep up with the state of the market while also achieving crucial workplace goals like productivity, coordination, and problem-solving. BIM may be able to assist with these important elements. Integrating intelligent objects into the model is the main benefit that BIM provides. The entire model is full of data as these smart objects have all the knowledge about a component, from its geometric details to how it interacts with other elements.
Due to their complexity, infrastructure projects frequently necessitate multidisciplinary collaboration. To facilitate effective planning and execution, BIM offers actionable project information at every stage. It enables visualization of the project’s scheduling (4D) and expenses (5D) from the construction phase.
Autodesk 2012
As it makes it simpler to coordinate components like steel and precast concrete and improves delivery, installation, and handling, BIM is gaining substantial advantages for structural projects needing scheduling and prefabrication. The process of getting a project ready for structural analysis software is more effective since information can be transmitted straight from the building model and design outcomes are saved in the building information model.
Effects of BIM Implementation on Structural Engineers
BIM has ample opportunity to offer in terms of structural design, particularly in terms of workflow analysis. A manual effort may be required to maintain coordination and documentation when using traditional procedures, which sometimes include producing structural design and construction records concurrently. By utilizing a single integrated BIM-based structural model that combines an analytical representation for multiple analyses with a physical representation for documentation and coordination, BIM lessens these problems. This strategy lessens the need for different models while enhancing a firm’s productivity, quality, and adaptability. BIM streamlines the procedure and enhances overall efficiency and flexibility through the efficient use of architectural designs.
Structural Modeling and Analysis using BIM
BIM software creates both analytical and physical representations of a computable building model, providing crucial data for external analysis applications. BIM and structural analysis tools must work together for this to happen, with the analytical model providing the essential data and the physical model accurately representing the project’s structure. The market leader in this sector is Autodesk Revit, which is fully interoperable with well-known analysis and design programs like Staad Pro, SAP2000, ETABS, and Robot Structural Analysis (RSA).
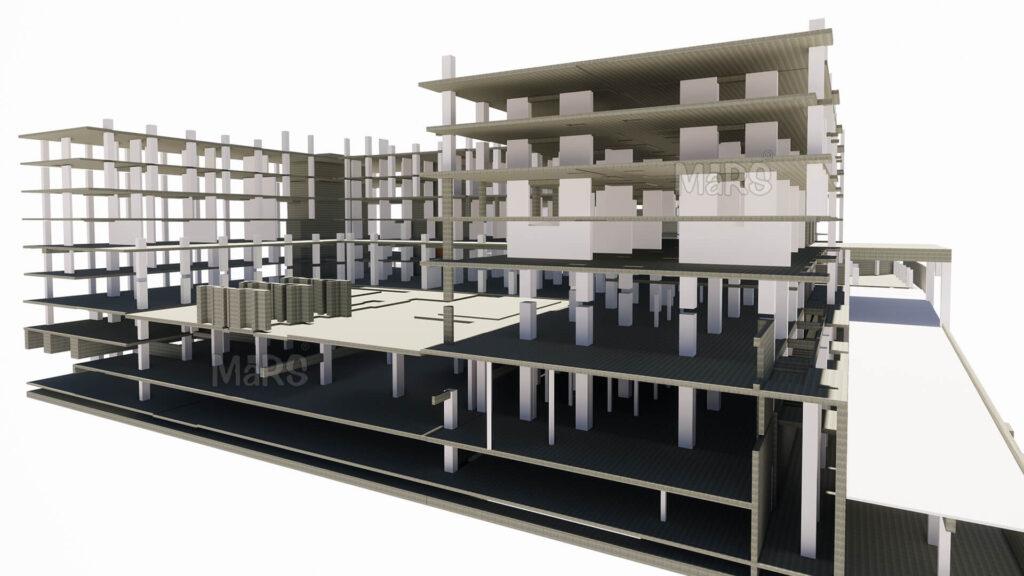
BIM enables accurate structural analysis during construction by combining time-dependent operations into a 4D structural model, avoiding potential dangers and conflicts. This approach is especially helpful for structures that change over time since it gives a complete picture of the structure, ensuring its effectiveness and safety.
4D Structural Model
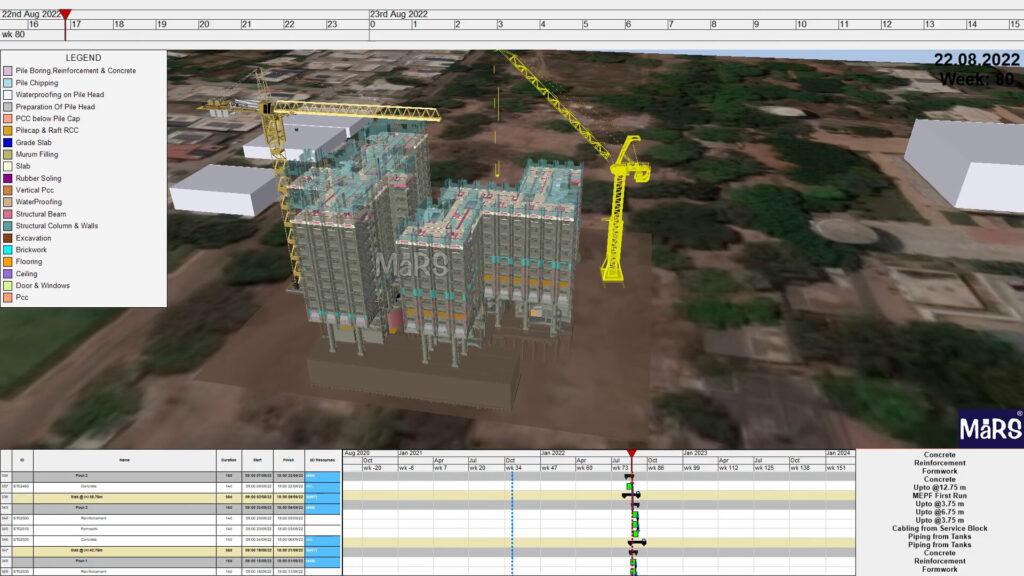
In addition to the project’s structural information, a 4D structural information model includes time-related data, such as reinforcement details, loading conditions, load types, timetables, construction activities, resources, and the amount of steel and concrete used.
Due to shifting material qualities and loading circumstances, structural analysis is essential during construction. More organizations are using this tactic as modern 3D modeling technology makes it possible for structural engineers and designers to build models for documentation and collaboration.
Using object-oriented programming, BIM software assembles structural parts. Tools for structural design based on BIM optimize designs, assess environmentally friendly options, and organize field activities and construction sequencing. It enables error-free fabrication and construction, and drawing checks take less time and effort.
Benefits of using BIM-based Structural Design
Building information models, according to Autodesk, enable structural engineers to plan, visualize, simulate, analyze, document, and build projects more correctly, efficiently, and cost-effectively. The most significant advantages of BIM-based structural designs are listed below.
1. Increased Productivity
Construction document production is automated using BIM, saving time and effort. 53 % of businesses consider BIM to be the optimal platform for construction documentation, according to a McGraw Hill Construction survey. By enabling engineers to make changes in a single location, BIM streamlines structural design, increasing productivity and improving the efficacy and efficiency of structural analysis.
2. Coordination and Better Data Management
By making it easier to produce construction documents and display the findings from structural analysis and design in a sharable way, BIM has a substantial impact on the documentation phase of a project. This enhances accuracy and minimizes errors by identifying coordination problems during the design phase.
3. Optimizing Structural Design via Simulation and Visualization
Before construction, decision-making is aided by simulation of installation, design, and workflow management. To model seismic events and their effects on infrastructure, BIM and real-time navigation are utilized. These techniques generate intricate structural models that help with problem identification and diagnostics and may perhaps lessen upcoming infrastructure challenges.
Conclusion
The process for structural design is greatly improved by BIM, which boosts productivity and efficiency. Engineers value BIM’s capacity to produce construction documentation automatically, which cuts down on detailing time and eliminates mistakes. Additionally, BIM makes it simple to share the outcomes of structural analysis, design, and documentation, assuring a centralized platform for sharing all project information.