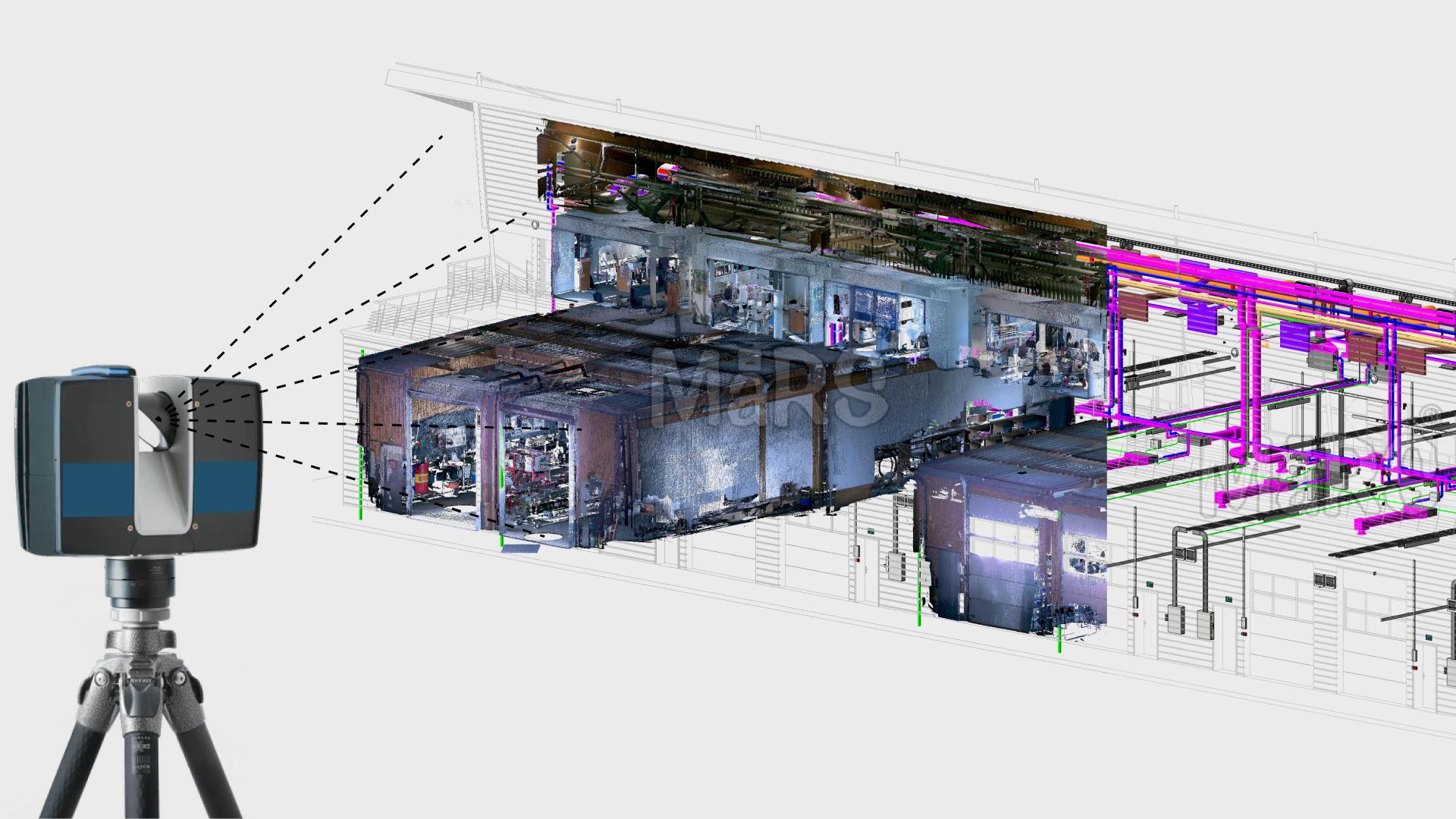
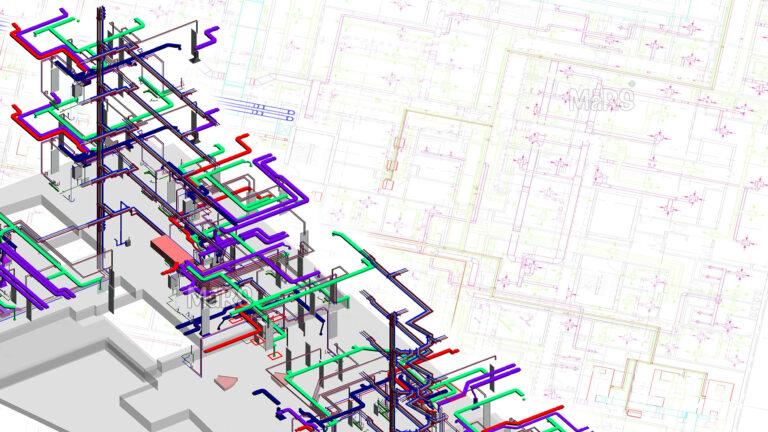
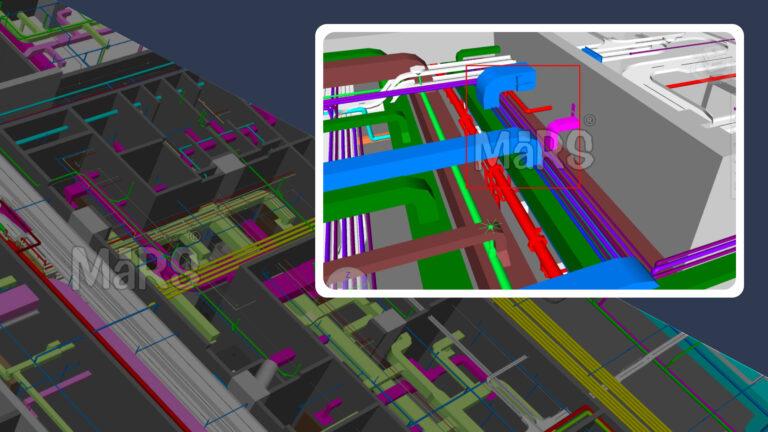
The significance of MEP systems has become quite evident today due to the complexity of modern buildings and the need for higher energy efficiency as well as sustainability. Owing to several issues raised by the traditional design process, construction, and maintenance, inefficiency results from it, therefore leading to wastage and increased environmental footprints.
The introduction of BIM is seen as an innovative solution that has revolutionized MEP systems throughout their lifecycle enabling better collaboration among stakeholders making informed decisions, and optimizing performance to enhance sustainability.
BIM helps in early-stage designs such as energy modeling or clash detection about energy efficiencies and optimization that should be achieved through a lessening of operations costs due to this project management method. It further provides support for risk mitigation regarding delayed activities as well as interferences related to maintaining operating assets which are critical for satisfying development goals set between developers and operators for a sustainable environment.
BIM in MEP Design: Optimizing from the Start
| BIM Feature | How it Enhances Sustainability | Benefits |
| Energy Modeling | Accurately Simulates Energy Performance of MEP Designs Before Construction. | Allows for selection of energy-efficient equipment, optimization of building orientation and envelope, and reduction of energy consumption throughout the building’s life cycle. |
| Clash Detection | Identifies Spatial Conflicts between MEP Components (e.g., ducts, pipes, conduits) in the virtual model. | Minimizes costly on-site rework, reduces material waste, and avoids delays caused by unforeseen conflicts during construction. |
| System Optimization | Assists in sizing MEP equipment based on actual load requirements and optimizing ductwork, piping, and electrical routing. | Prevents oversizing of equipment, leading to energy Savings, and ensures efficient flow of fluids and electricity, reducing energy losses. |
| 3D Visualization | Provides a clear and intuitive representation of MEP Systems within the building context. | Facilitates better communication and collaboration among stakeholders, leading to informed decision-making and reduced design errors. |
| Parametric Modeling | It enables designers to create flexible MEP components that can be easily adjusted to accommodate changes in the building design. | Reduces the need for time-consuming manual adjustments, and improves design flexibility of alternative design solutions. |
For MEP Engineering Services, BIM is a powerful tool for modelling and analyzing complex systems. It maximizes energy efficiency by creating a digital twin in the building, reduces operating costs, and can replicate and consider design possibilities Furthermore, BIM reduces the potential for major changes during construction through MEP planning to integrate with other disciplines and help identify any conflicts.
BIM in MEP Construction: Streamlining and Reducing Waste
MEP BIM is vital during the construction of MEP systems, which supports prefabrication, installation coordination, logistics, and material management. Through detailed models, the BIM provides accurate information regarding components that can be used for MEP thus, enabling manufacturing to occur in a controlled factory environment. This reduces wastage at the site, speeds up the time of installation, and enhances quality control. These components coming in as whole units minimize waste and emissions. Besides facilitating the proper installation of components in the correct positions, BIM also reduces errors and costs associated with repair work. By integrating with project schedules, BIM creates 4D models that show installation sequences and highlight conflicts thereby avoiding interference and making work smoother. In addition to this, BIM helps with other activities such as logistics and materials management where it saves on excess purchases while optimizing delivery schedules to cut on CO2 emissions produced by transport systems.
BIM in MEP Operation: Maintaining Efficiency
The long-life sustainability of MEP systems in a building relies on a critical phase known as operational development. In this regard, BIM has come into play through the digital twin concept that entails real-time data from sensors and building management systems (BMS) representing a replica of the building. This dynamic model can be used to capture information on MEP equipment performance thus enabling proactive maintenance and optimizations.
The digital twin and BIM also enable predictive maintenance which reduces reactive maintenance requirements and extends equipment lifespan thereby lowering the impact on the environment due to replacements. By integrating BIM models with BMS, facility managers can create an integrated energy management platform that enables them to monitor consumption patterns for energy, identify inefficiencies in MEP system settings, and optimize them for maximum energy savings. One example is adjusting HVAC settings according to occupancy levels or weather conditions through automation.
BIM’s Contribution to Overall Building Sustainability Goals
The overall sustainable aim of this technology is achieved by the aggregated effect of BIM on an MEP system in its lifecycle. By minimizing wastage in design, construction and operation, it cuts back on resource usage such as raw materials, water, and energy. This serves to enhance the MEP system performance through energy modelling, equipment sizing and predictive maintenance thus increasing the energy efficiency that would lower a building’s carbon footprint during operation.
BIM encourages collaboration and data-driven decision-making which promotes holistic approaches towards sustainability. It allows stakeholders to analyze the Environmental impacts related to MEP systems throughout their lifespan beginning with embodied energy of construction materials to operational energy consumption. This broad view leads to better decisions and stronger commitments to sustainability. By way of illustration, BIM models may help to evaluate the viability of solar photovoltaic systems, optimize their placement and orientation, and flawlessly incorporate them into a building’s electrical system.
Conclusion
The complexity of contemporary buildings coupled with the rising demand for energy efficiency and sustainability has underscored the significance of MEP systems. BIM has been identified as a game changer by enabling stakeholders to optimize energy performance reduce wastage and make informed decisions during the design phases construction phases as well as operation stages. This extends to include such things as clash detection in energy modelling prefabrication expedited installation predictive maintenance and operational energy management thus contributing towards a greener more sustainable built environment.