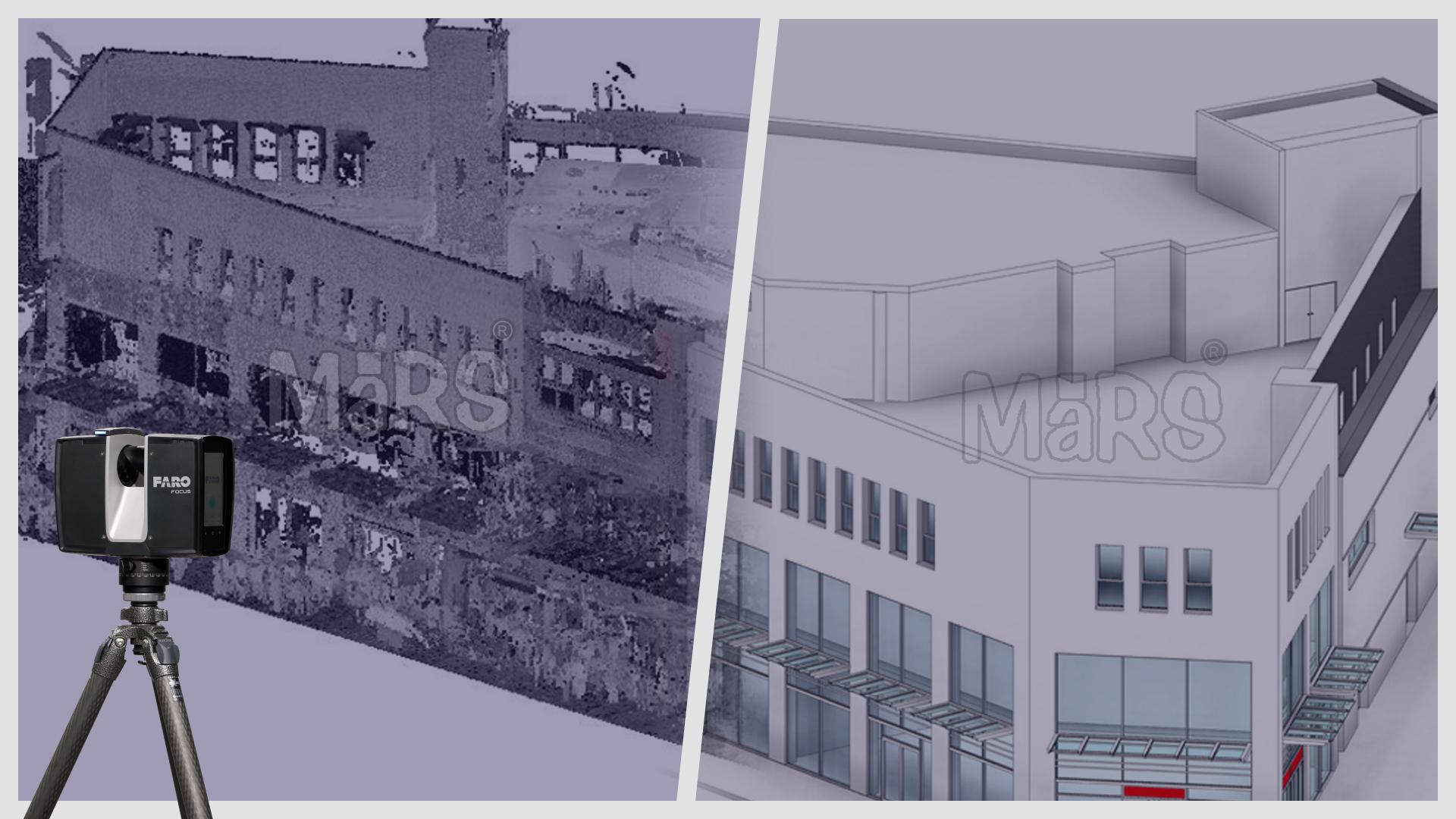
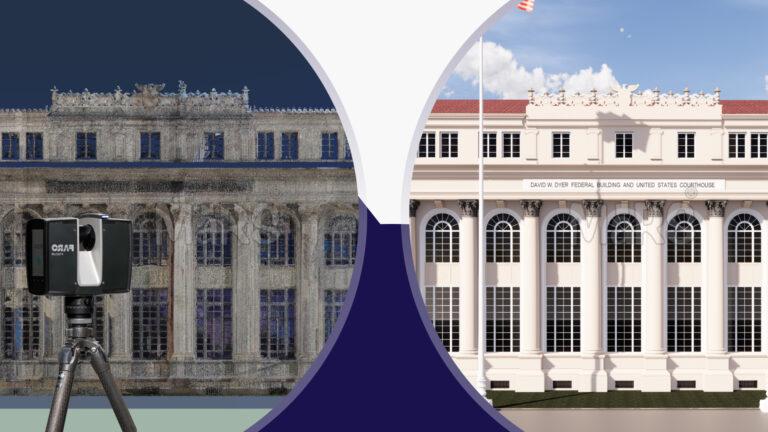
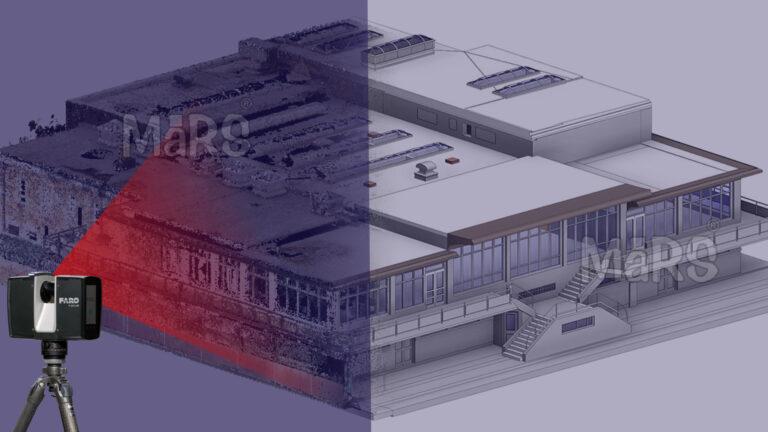
Scan to BIM technology has revolutionized how we convert raw data into actionable insights. This advanced process captures detailed measurements of physical spaces using tools like 3D laser scanners and drones. By transforming these measurements into digital point clouds, Scan to BIM technology creates accurate 3D models of environments. These models provide a solid foundation for strategic planning and decision-making in various sectors, from architecture to facility management.
Converting raw data into strategic solutions involves more than just capturing information. It requires processing and interpreting the data to derive meaningful insights. Point Cloud to BIM Services, a crucial component of Scan to BIM technology, enhances design accuracy, improves project planning, and supports efficient collaboration among team members. By employing these advanced techniques, businesses can turn complex data into practical solutions that drive better project outcomes and operational efficiency.
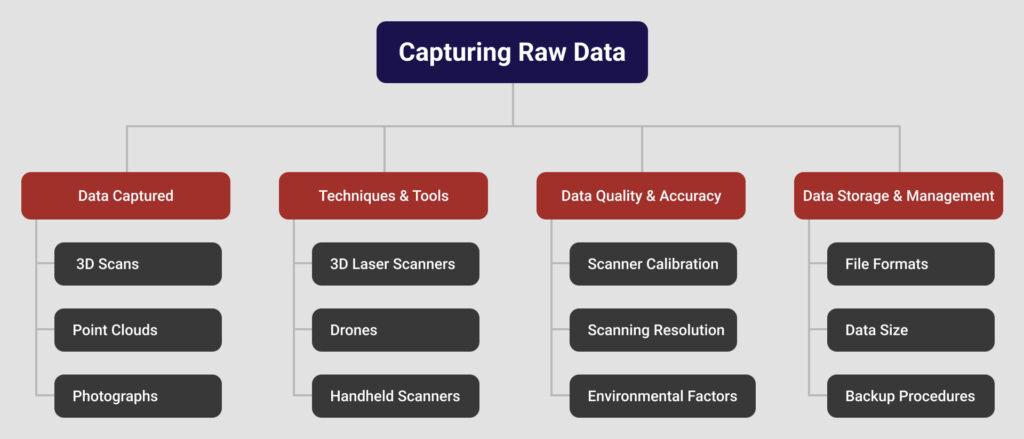
Capturing Raw Data
Scan to BIM starts with capturing data through various tools. 3D laser scanners and drones collect precise measurements of physical spaces. This data forms point clouds, which represent the scanned environment. The quality of this data depends on the scanning equipment and techniques used. High-quality scans lead to better models.
Types of Data Captured
- 3D Scans: Collect detailed spatial information from physical environments.
- Point Clouds: A collection of points in space representing surfaces of objects and spaces.
- Photographs: Supplementary images for texture and color details.
Techniques and Tools
- 3D Laser Scanners: Use lasers to capture precise measurements and create point clouds.
- Drones: Equipped with cameras and sensors to scan large areas from the air.
- Handheld Scanners: Portable devices for scanning smaller or hard-to-reach areas.
Data Quality and Accuracy
- Scanner Calibration: Ensure scanners are properly calibrated for accurate data.
- Scanning Resolution: Choose appropriate resolution for detail level required.
- Environmental Factors: Consider lighting and surface conditions affecting data capture.
Data Storage and Management
- File Formats: Save data in compatible formats like .e57 or .las for processing.
- Data Size: Manage large files efficiently to avoid storage issues.
- Backup Procedures: Regularly back up data to prevent loss.
Processing Raw Data
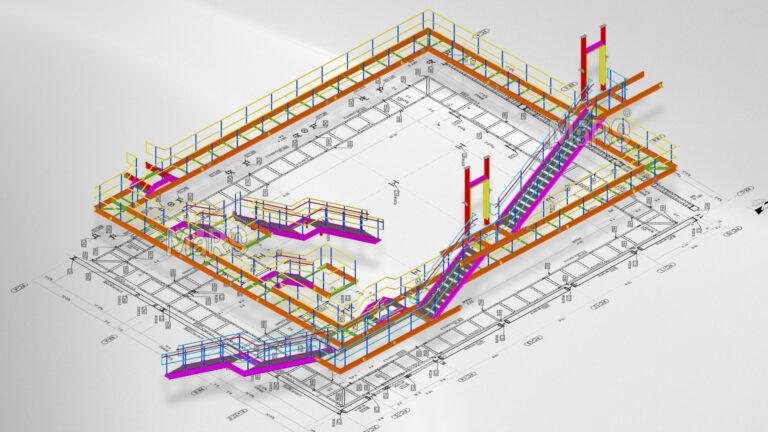
Once captured, raw data needs processing. This involves cleaning and organizing the point clouds. Software converts these clouds into detailed BIM models. This process helps in creating accurate digital representations of physical spaces. Tools like Autodesk Revit and Navisworks are commonly used for this transformation.
Strategic Advantages of Scan to BIM
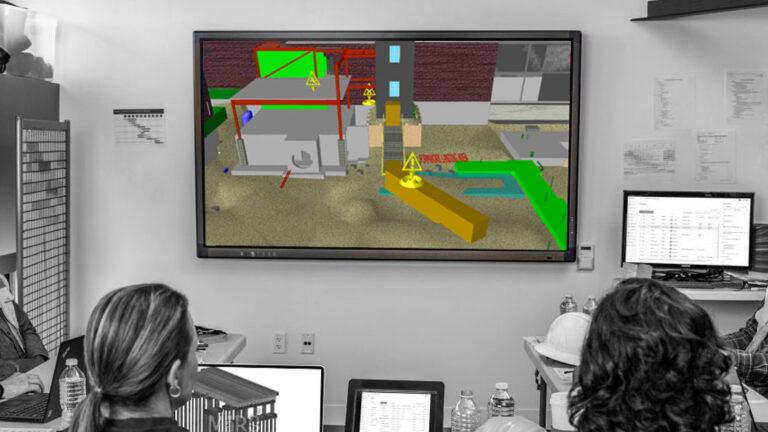
Scan to BIM offers several strategic advantages. It improves the precision of designs and plans. This accuracy helps in effective project planning and execution. The technology supports real-time collaboration among team members. It also aids in making informed decisions quickly.
Applications of Scan to BIM in Various Sectors
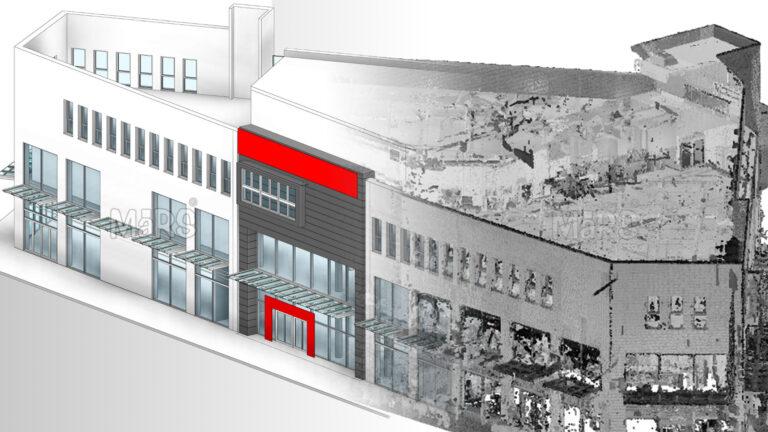
Scan to BIM technology applies to many fields. In architectural design, it aids in renovation and new projects. For infrastructure projects, it provides detailed models for construction. Facility managers use it for maintenance and operations. Each sector benefits from the enhanced accuracy and efficiency of Scan to BIM.
Data conversion with Scan to BIM can face challenges. Issues may arise with data quality or integration. To overcome these, use high-quality scanners and robust software. Follow best practices for data management. Address problems early to ensure accurate and useful outcomes.
Conclusion
Scan to BIM technology transforms raw data into valuable strategic solutions. It enhances design precision, planning, and collaboration. By adopting Scan to BIM, projects can achieve better results. Embracing this technology will lead to more effective and efficient outcomes.