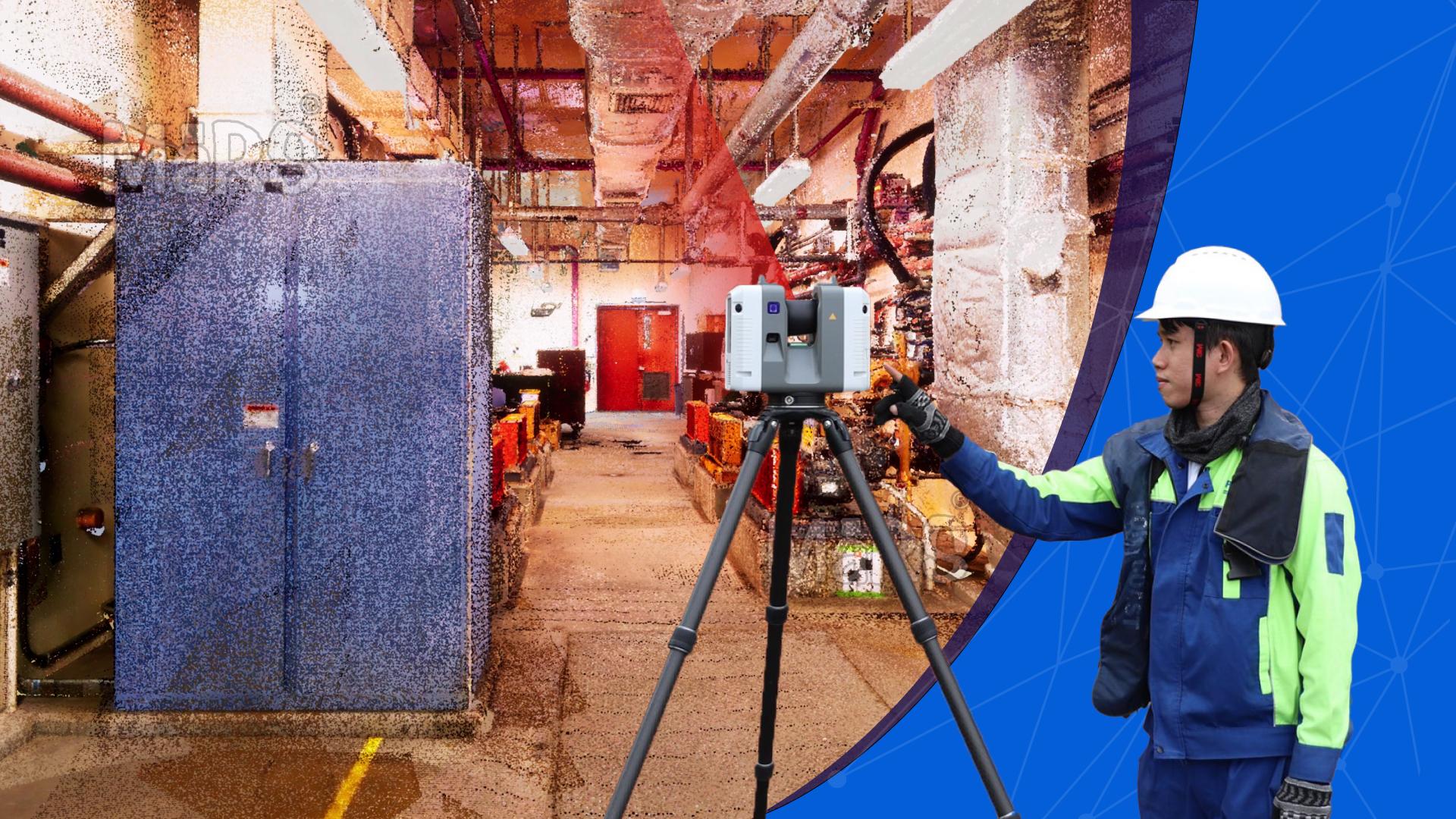
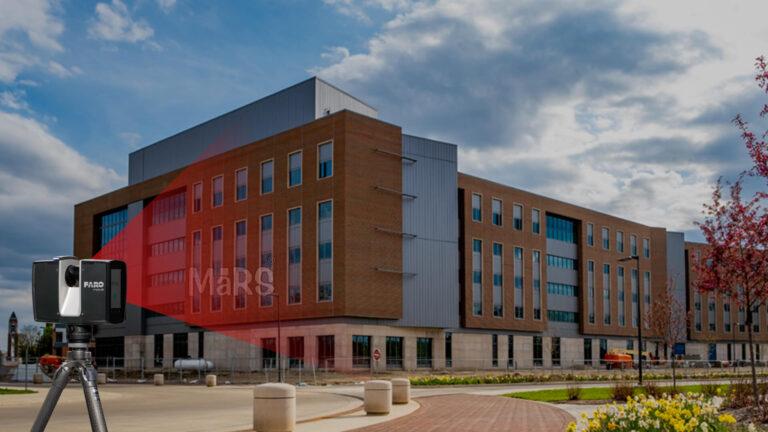
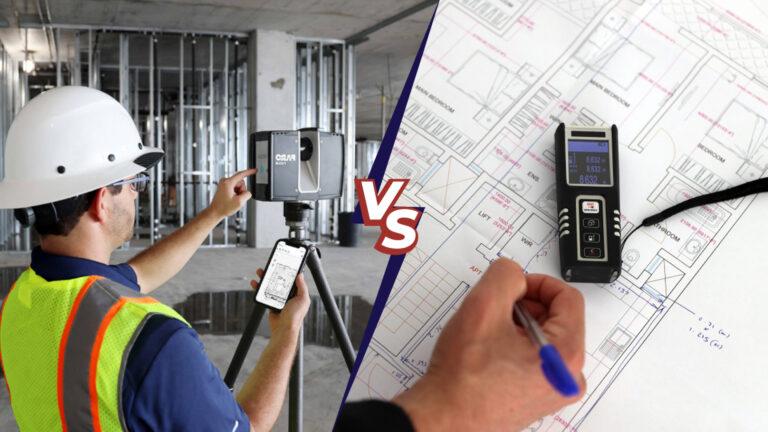
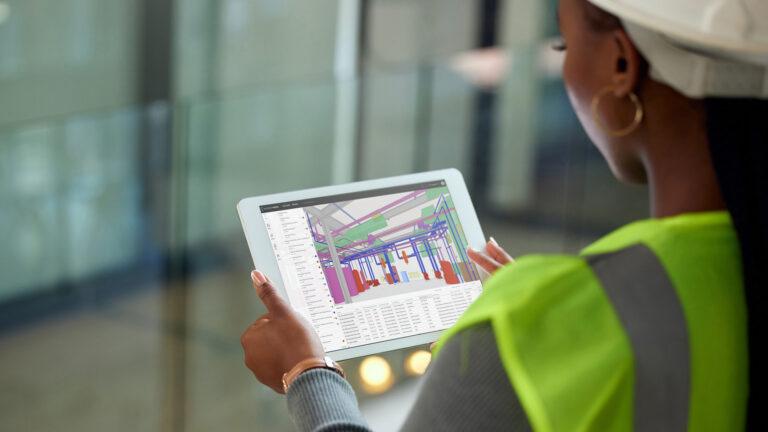
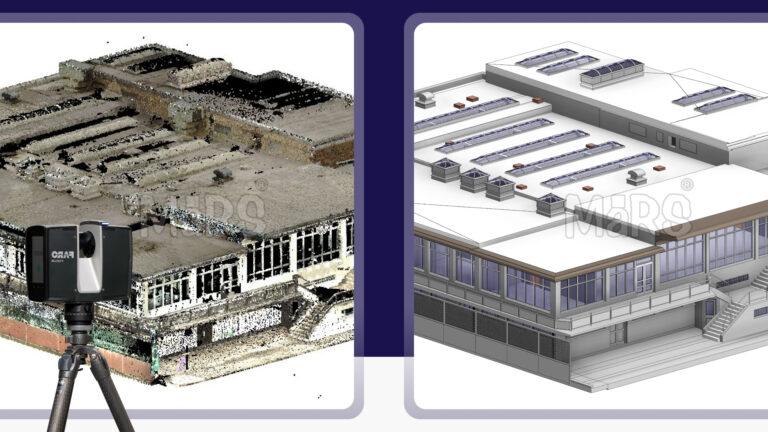
3D laser scanning is a powerful technology that captures precise spatial data to create detailed 3D models of physical spaces. This advanced method uses laser beams to measure distances accurately, producing a “point cloud” of data points that represent the physical environment. These data points are then processed with specialized software to generate detailed and accurate 3D models. The key components of 3D laser scanning include the laser scanner, which emits and receives laser beams the scanning software, which processes the captured data and data processing tools, which refine and convert the data into usable 3D models.
Beyond the construction industry, facility managers and building owners can leverage 3D laser scanning for effective maintenance and renovation projects. The high level of accuracy makes it easier to plan upgrades and improvements while reducing risks during project execution. Additionally, industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, and heritage conservation can utilize 3D laser scanning to document and analyze complex structures, machinery, and historical buildings. By capturing precise spatial data, these sectors can better manage resources, streamline workflows, and preserve critical information for future needs.
Applications of 3D Laser Scanning
The applications of 3D laser scanning Services are vast and diverse. This technology is used to create precise 3D models of various physical spaces, ranging from small architectural features to large infrastructure projects. In architecture, 3D scanning provides accurate site surveys, which are crucial for effective planning and design. In construction, it assists in creating as-built models and detecting clashes between systems. Facility managers use it for space optimization and asset management. Each application benefits from the detailed and reliable data that 3D scanning provides, which improves project outcomes and decision-making across industries.
Manufacturing plants use 3D laser scanning for equipment layout optimization and to document existing conditions for retrofitting or expansion projects. The healthcare industry utilizes it to design complex hospital layouts, while historical preservation efforts benefit from the detailed documentation of heritage sites. Additionally, facility managers employ the technology to streamline maintenance planning, track asset conditions, and manage renovations efficiently.
Architects

Accurate Site Surveys
For architects, 3D laser scanning offers a significant advantage in conducting site surveys. By capturing detailed and accurate representations of existing conditions, architects can plan and design with greater precision. This reduces the likelihood of errors during the design phase, ensuring that plans are based on reliable data. For example, scanning can capture the exact dimensions of a site, including complex features, which helps architects design structures that fit perfectly within the existing environment.
Design Precision
Design precision is another critical benefit of 3D scanning for architects. Detailed 3D models enable architects to make accurate modifications to existing structures or create new designs that integrate seamlessly with their surroundings. This technology supports complex design tasks, such as integrating new buildings into historic settings or retrofitting existing structures. By providing a detailed and accurate representation of the site, 3D scanning enhances the overall design process.
Engineers

Structural Assessments
Engineers rely on 3D scanning for accurate structural assessments. This technology provides detailed data that allows engineers to evaluate the integrity and stability of structures. The precision of the scanned data enhances structural analysis and modeling, leading to better-informed decisions about maintenance, repairs, and upgrades. For example, engineers can use scanning data to assess the condition of bridges, buildings, or other infrastructure, identifying potential issues before they become critical.
Monitoring and Inspection
Ongoing monitoring and inspection of infrastructure are also improved by 3D scanning. The technology allows engineers to track changes over time and detect potential problems early. Regular scans can reveal issues such as shifting foundations or structural wear, enabling proactive maintenance and preventing costly repairs. For example, a periodic scan of a bridge can help engineers identify signs of deterioration that may need attention.
Construction Professionals

As-Built Models
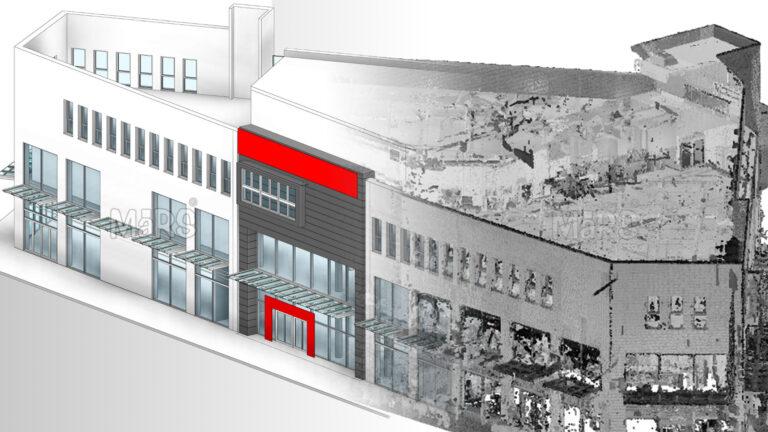
For construction professionals, 3D scanning provides detailed as-built models that serve as a reference throughout the construction process. These models help verify that the construction matches the design specifications. By comparing the as-built model with the design, construction teams can ensure that all elements are correctly installed and make adjustments as needed. This reduces the risk of errors and discrepancies that could lead to costly rework.
Clash Detection and Coordination
3D scanning plays a crucial role in BIM Clash detection and coordination. The technology helps identify conflicts between different systems and components, such as plumbing, electrical, and HVAC systems. By detecting these clashes early, construction teams can resolve issues before they affect the project’s timeline or budget. This improves collaboration among different trades and disciplines, leading to smoother project execution.
Mitigating Construction Challenges
Real-world examples highlight how 3D scanning has solved construction challenges. In complex projects, scanning has been used to address issues such as misalignment of structural elements or conflicts between systems. By providing accurate data, 3D scanning helps avoid delays and cost overruns, leading to more successful project outcomes.
Facility Managers

Space Management
Facility managers benefit from 3D scanning through improved space management. Scanning provides detailed data on the layout and dimensions of spaces, which helps in optimizing space usage and planning future modifications. For example, facility managers can use scanning data to design efficient office layouts or plan for new equipment installations.
Asset Management
Asset management is another area where 3D scanning proves valuable. Detailed records of facility components and systems are captured through scanning, facilitating maintenance and operational management. Facility managers can track assets, plan for upgrades, and manage space more effectively with the accurate data provided by scanning.
Improvements Through Scanning
Examples of improvements in facility management due to 3D scanning include more efficient maintenance scheduling and better planning for facility upgrades. Scanning helps facility managers make informed decisions about managing and maintaining their facilities, leading to enhanced operational efficiency.
Historical Preservationists

Preserving Historical Structures
Historical preservationists use 3D scanning to capture detailed records of historic buildings. This technology supports accurate restoration and preservation efforts by providing a precise representation of the building’s current condition. Scanning helps in documenting architectural details that are essential for maintaining the building’s historical integrity.
Restoration Projects
In restoration projects, 3D scanning provides critical data for reconstructing damaged or deteriorated structures. For example, scanned data can guide the restoration of intricate architectural features, ensuring that they match the original design. Successful restoration projects have demonstrated the value of scanning in preserving historical accuracy.
Impact on Preservation Efforts
The impact of 3D scanning on preservation efforts is significant. Case studies show how scanning has enhanced documentation and research of historical sites. By providing detailed and accurate records, scanning supports the preservation of cultural heritage and contributes to historical research.
Real Estate Developers

Property Evaluations
Real estate developers use 3D scanning for accurate property evaluations. Scanned models provide detailed data on property conditions, which helps in assessing value and potential. This information is crucial for making informed investment decisions and setting realistic property values.
Development Planning
In development planning, 3D scanning assists in designing new projects and renovations. The technology integrates with marketing tools to create virtual tours and presentations, showcasing properties effectively. Developers can use scanning data to plan and execute developments with greater precision.
Marketing and Virtual Tours
3D scanning enhances marketing efforts through virtual property tours. Real estate projects can use scanned models to attract buyers or tenants with interactive and detailed presentations. This technology helps in showcasing properties and highlighting their features in a compelling way.
Urban Planners

Urban Development
Urban planners integrate 3D scanning into city planning and development strategies. Scanning provides detailed models of existing urban environments, which helps in planning new developments and improving urban spaces. This technology supports the creation of more efficient and functional urban areas.
Topographic Surveys
For topographic surveys, 3D scanning captures accurate data on land contours and features. This information assists in evaluating land use and infrastructure needs. Urban planners use scanned topographic data to design better layouts and plan for future developments.
Smart City Planning
In smart city planning, 3D scanning contributes to creating efficient urban environments. The technology helps in designing and implementing smart infrastructure solutions. Examples show how scanning has enhanced urban planning projects and supported the development of smart cities.
Surveyors

Land Surveying
Surveyors benefit from 3D scanning by improving land measurements. The technology provides precise data on property boundaries and land features. This enhances the accuracy of land surveys and reduces errors in property boundary determinations.
Topographic Mapping
3D scanning supports topographic mapping by providing accurate data on land elevations and contours. This information enhances the accuracy of topographic maps and survey reports. Surveyors use scanned data to create detailed and reliable maps.
Boundary Surveys
In boundary surveys, 3D scanning improves accuracy and reduces disputes. Scanned data provides detailed measurements of property boundaries, helping to resolve conflicts and ensure accurate property determinations. Case studies illustrate the benefits of scanning in boundary surveys.
Manufacturers

Reverse Engineering
Manufacturers use 3D scanning for reverse engineering existing parts. Scanning creates detailed models that can be used for redesign or replication. This enhances accuracy in the reverse engineering process and supports the development of new products.
Quality Control
Quality control is improved with 3D scanning by providing detailed measurements of manufactured products. Scanning helps ensure that products meet design specifications and facilitates comparison between designed and manufactured parts.
Design Verification
In design verification, 3D scanning supports the accuracy of product development. The technology helps in confirming that manufactured parts match the intended design. Examples show how scanning has improved manufacturing processes and product efficiency.
Conclusion
3D laser scanning benefits a wide range of professionals, including architects, engineers, construction workers, facility managers, preservationists, developers, planners, surveyors, and manufacturers. Each group gains from the technology’s ability to provide detailed and accurate data, which improves project outcomes and decision-making.