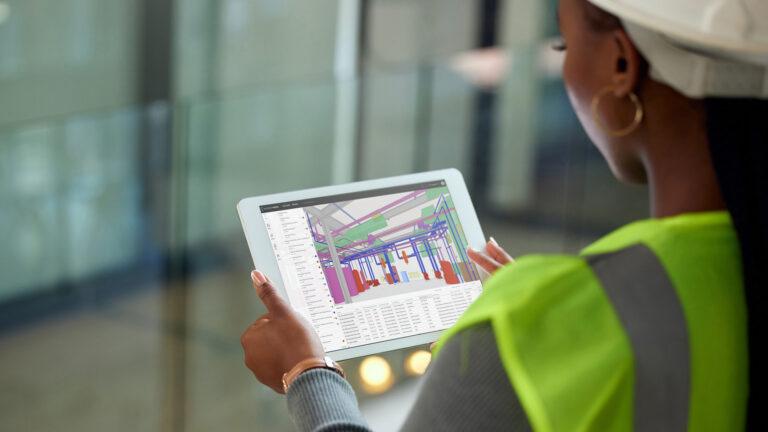
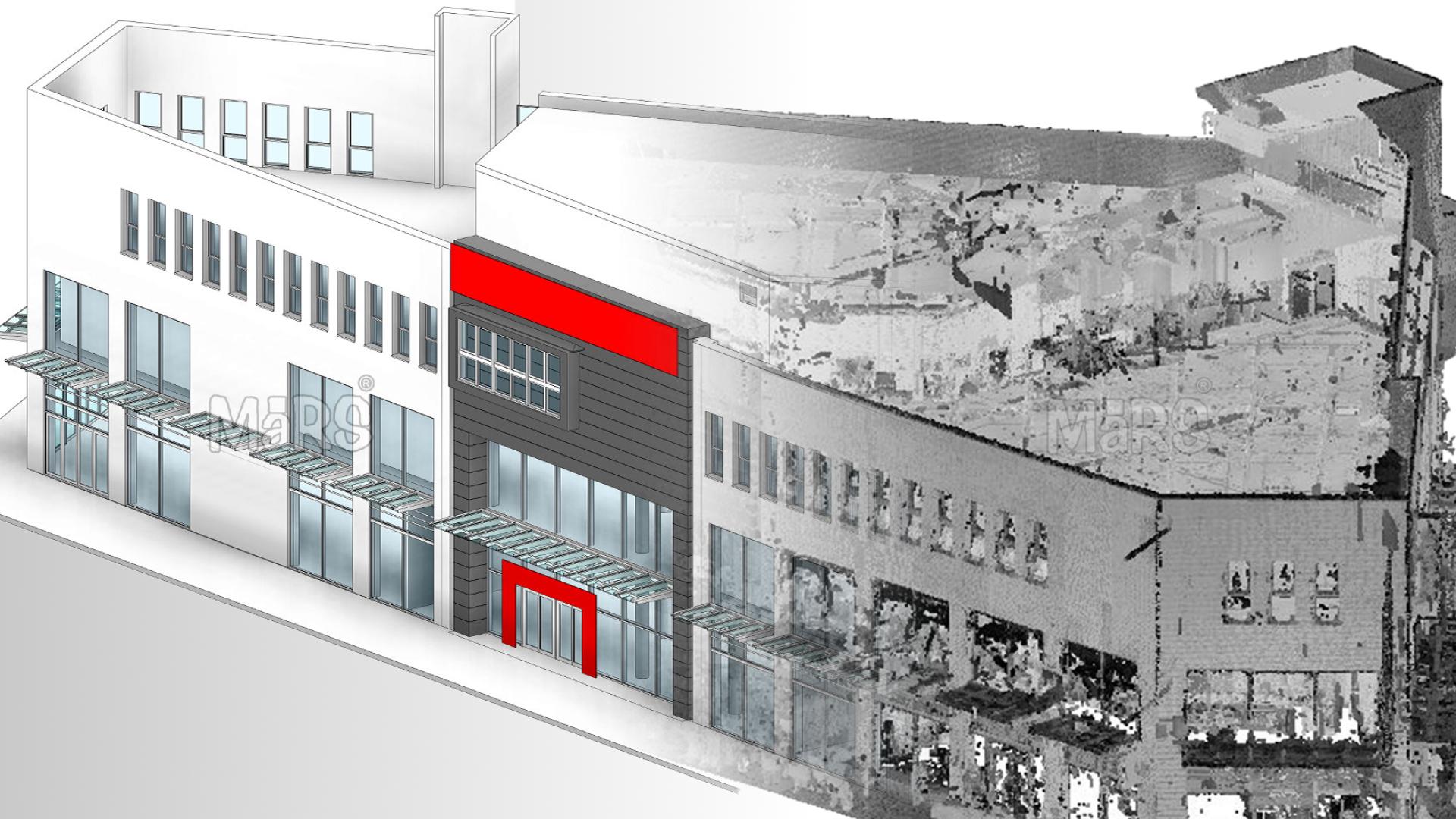
A new technology is changing everything that used to be just an idea. This method of data collection applies laser scanning or photogrammetry to the procurement of actual real-world conditions about buildings with so much precision regarding details. After this, all this information is turned into a 3D Structure that provides an abundance of information for decision-makers in the course of the project. Scan to BIM ensures that as-built models are precise, time-saving, and convenient since it allows the correction of any inaccuracies, therefore saving time throughout the lifecycle and reducing costs significantly during completion. The article delves into Scan to BIM principles, workflow, and its significance to as-design documentation.
What is Scan to BIM?
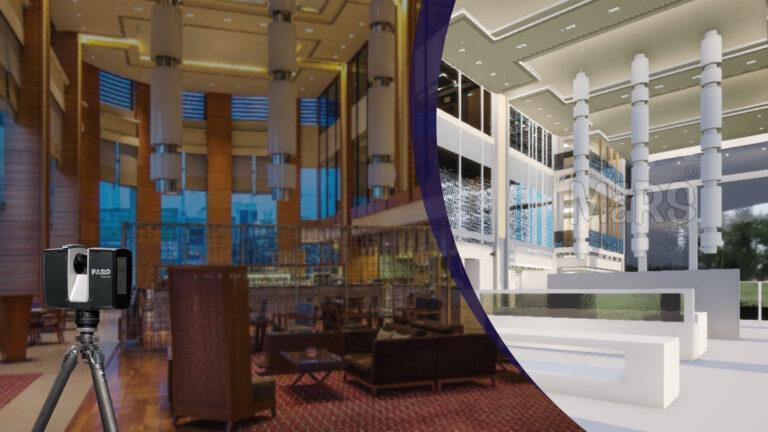
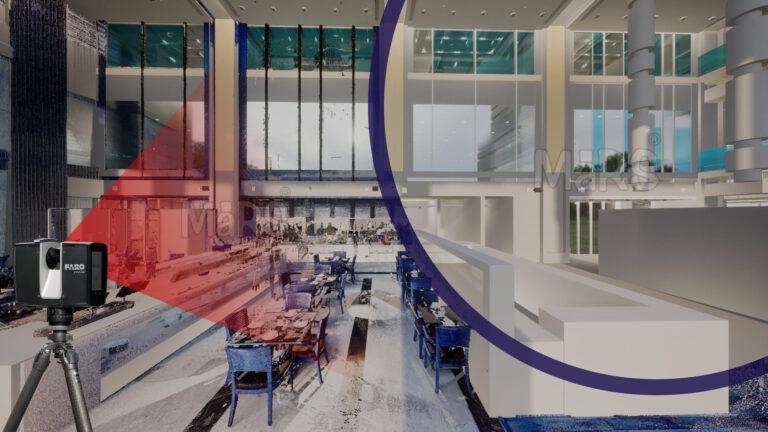
Laser Scanning
To do this, laser beams are sent out by a laser scanner, and then the beams sweep across all surfaces of the structure systematically. The scanner computes a dense “point cloud” that consists of millions of useful data points. These points accurately represent the spatial coordinates as well as the dimensions of the structure and are generated by measuring the time taken for these beams to bounce back.
Photogrammetry
Photographs taken from different angles and overlapping each other are needed to produce a three-dimensional structure. The photographs are then analyzed by specialized software to establish common points and features for constructing a highly detailed point cloud.
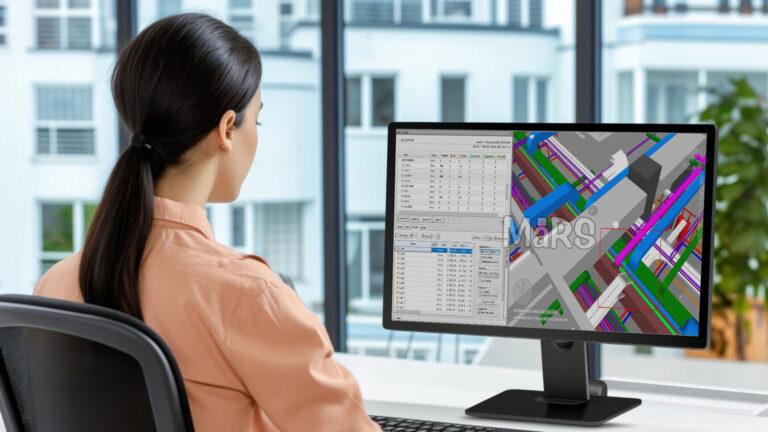
The resulting point cloud serves as the foundation for Point Cloud to BIM, regardless of how it is gathered. To get rid of any noise, this raw data is carefully treated, cleansed, and filtered. Prominent BIM software platforms include Graphisoft ArchiCAD and Autodesk Revit.
Benefits of Scan to BIM for As-Built Models
Unrivaled Precision
This technology’s ability to capture millions of accurate data points makes it possible to achieve accuracy that would be impossible with manual measurements. This attribute is very important in renovation projects where even the slightest discrepancies may result in expensive rework.
Streamlined Efficacy
By automating a large portion of the data collecting and processing, scanning to BIM significantly reduces the time and effort required to create Point Cloud to BIM. As a result, there are notable cost reductions and quicker project completion timeframes.
Reduction of Errors
Inaccuracies that stem from human errors inherent in manual surveying are reduced through Scan to BIM. Any risk associated with transcription errors is eliminated because the process is digitized, ensuring uniformity throughout the model.
Clash Detection and Resolution
When new designs are introduced into existing buildings, BIM facilitates early detection between those designs using conflict checking between the as-built & proposed design. Such identification allows for resolution during the design stage hence saving construction time & cost.
Sustainability
Materials can be reused and waste reduced through Scanner to BIM, which can help in sustainability efforts. Accurate evaluations of existing structures enable designers and contractors to identify where materials can be repurposed resulting in less consumption of new materials.
Scan to BIM As-Built Models
Renovation And Retrofitting
As-built models provide detailed knowledge of the structure’s layout, dimensions, and systems that form the basis of successful renovation or retrofitting projects. Architects and engineers use this information to integrate their designs seamlessly into such structures.
Facility Management
Scanning the building and developing as-built allow for creating computerized prototypes of the building by showing a lot of information on how to preserve, operate, and utilize space. For this reason, facility managers can use these models to optimize maintenance schedules, monitor asset life cycles, and simplify space planning.
Construction Verification
It involves comparing the actual Scan to BIM with the original design intent to facilitate strict construction verification. This aids in recognizing any deviations from design thus ensuring that the final structure meets required specifications and quality standards.
Digital Twins for Smart Buildings
Digital twins as real-time virtual replicas of both physical structures and their systems. Advanced facilities management, energy optimization, predictive maintenance, and occupant experience improvement are some benefits of such digital twins provided they are used in constructing structures.
Conclusion
The construction lifecycle is now being changed by Scan to BIM which comes with no equal precision, speed, and teamwork for getting as-built models. This technology replaces traditional approaches thereby giving stakeholders exact information on a specific topic that enhances their decision-making process leading to the smooth flow of activities and finally successful projects. With digital transformation gaining momentum in the construction sector, Scan to BIM is expected to be an essential method for making the built environment more effective, environmentally friendly, and resistant.