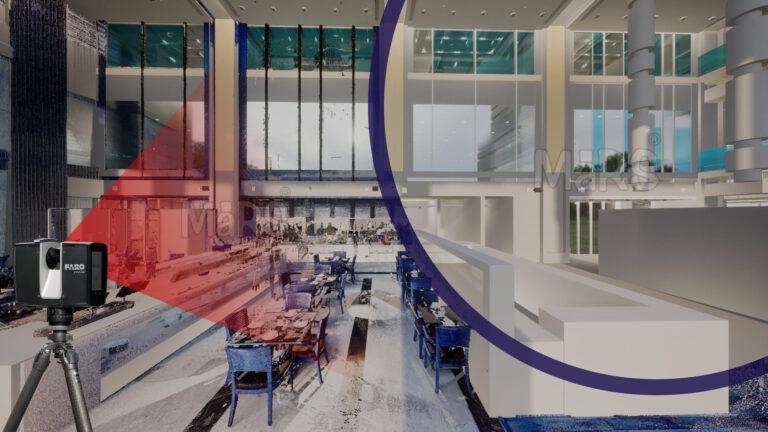
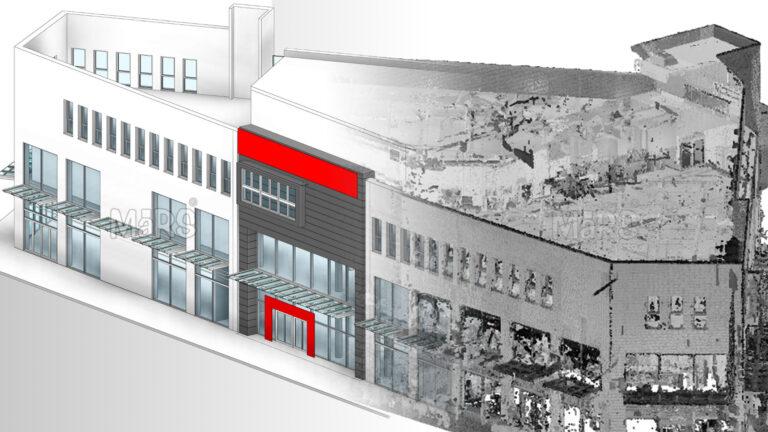
Scan to BIM has emerged as a transformative technology that helps capture detailed 3D data of existing structures, converting it into accurate digital models. This guide will walk you through the process of implementing Scan to BIM, highlighting the essential steps to ensure a smooth and effective integration.
Understanding the Basics
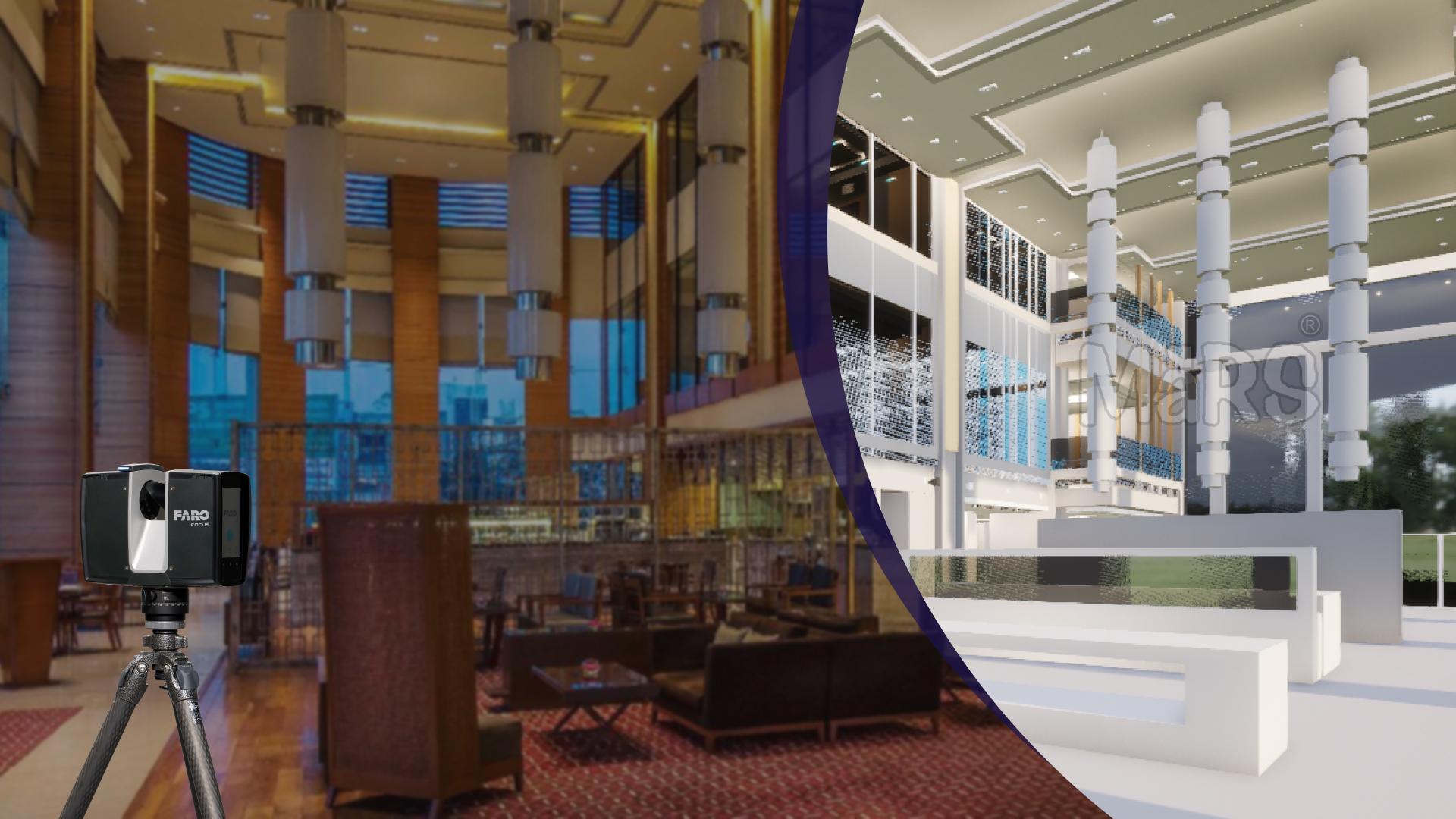
Before diving into the implementation process, it’s essential to grasp what Revit Scan to BIM entails. Essentially, Scan to BIM combines laser scanning technology with BIM software to create detailed 3D models of existing buildings. These models reflect the actual conditions of a structure, providing a reliable basis for renovation, facility management, and new construction.
Setting Clear Objectives
The first step in the Scan to BIM process is defining your project’s goals. Understanding what you aim to achieve with Scan to BIM will guide your decisions throughout the project. Are you looking to document as-built conditions for renovation purposes? Or are you enhancing facility management capabilities? Maybe your goal is to support new construction with accurate data. Clear objectives will help you select the right tools and strategies for your needs.
Choosing the Right Technology
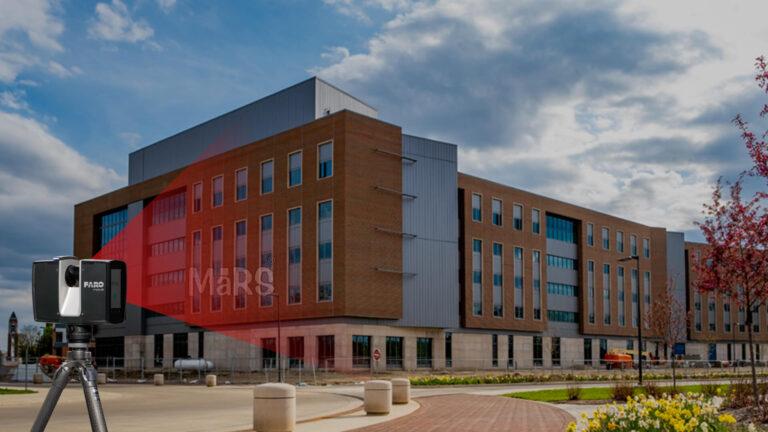
- Laser Scanners: These devices capture precise measurements of physical objects by recording millions of points to create a point cloud. Laser scanners are ideal for detailed and accurate data collection, especially for complex structures.
- Photogrammetry: This technique involves taking multiple photographs of a structure and using software to create a 3D model. It’s particularly useful for capturing textures and colors.
- Drones: Drones can quickly capture large areas or difficult-to-reach locations, making them suitable for expansive or high-rise buildings.
Planning the Scanning Process
- Scanning Locations: Identify the key areas of the building that need to be scanned. Consider the layout and any obstacles that might affect data capture.
- Angles and Coverage: Determine the best angles and positions for scanning to ensure that all relevant details are captured. Aim for complete coverage to avoid gaps in the data.
- Accessibility and Conditions: Assess the site conditions, including lighting and accessibility, to plan the scanning process effectively. Address any potential issues that could impact the quality of the scan.
Executing the Scan
- Calibrate Equipment: Properly calibrate your scanning equipment according to the manufacturer’s guidelines. Accurate calibration is essential for reliable data capture.
- Conduct Scanning: Follow your plan and systematically capture data from all identified locations and angles. Pay attention to details and ensure that you cover every required area.
Processing and Registering Data
- Data Registration: This involves aligning and merging multiple scans into a unified dataset. Specialized software helps in this process, ensuring that all scans are accurately combined to form a complete point cloud.
- Creating the 3D Model: Convert the registered data into a 3D BIM model using BIM software. This model should reflect all the features and dimensions of the building, providing a detailed and accurate digital representation.
Reviewing and Refining the Model
- Verify Accuracy: Compare the BIM model with the original scans to ensure it accurately represents the building. Check for any discrepancies or missing details and make necessary adjustments.
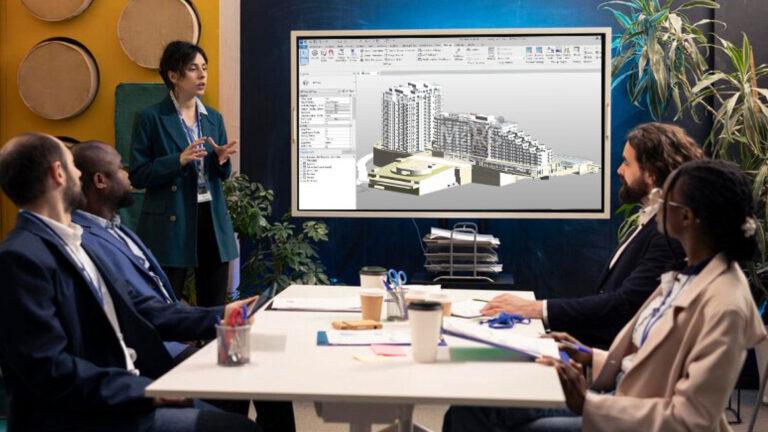
- Stakeholder Feedback: Share the model with project stakeholders, including architects, engineers, and clients. Incorporate their feedback to refine the model and address any concerns.
Integrating the Model into Your Workflow
- Update Documentation: Incorporate the BIM model into your project plans and documentation. It will serve as a valuable reference throughout the project lifecycle.
- Team Training: Ensure that your team is trained to use the BIM model effectively. Provide resources or training sessions to help them understand how to leverage the model for their specific tasks.
Maintaining and Updating the Model
- Regular Updates: As the project progresses or changes occur, update the model accordingly. Regular maintenance ensures that the model remains accurate and reflects the current state of the building.
- Future Use: Utilize the BIM model for future projects or facility management. An accurate digital representation of the building can provide valuable insights and support decision-making.
Conclusion
Implementing Scan to BIM involves a series of well-defined steps, from setting objectives and choosing the right technology to executing the scan and refining the model. By following this comprehensive guide, you can effectively integrate Scan to BIM into your projects, enhancing accuracy and streamlining workflows. Embrace the power of Scan to BIM and transform your approach to building design, renovation, and management.